Did you know that chloride damage to concrete is one of the most persistent problems affecting concrete structures? From bridges to parking garages, chlorides can severely damage concrete and shorten its lifespan. But what exactly is chloride damage and how do you solve it?
Chloride damage concrete
What is chloride damage to concrete?
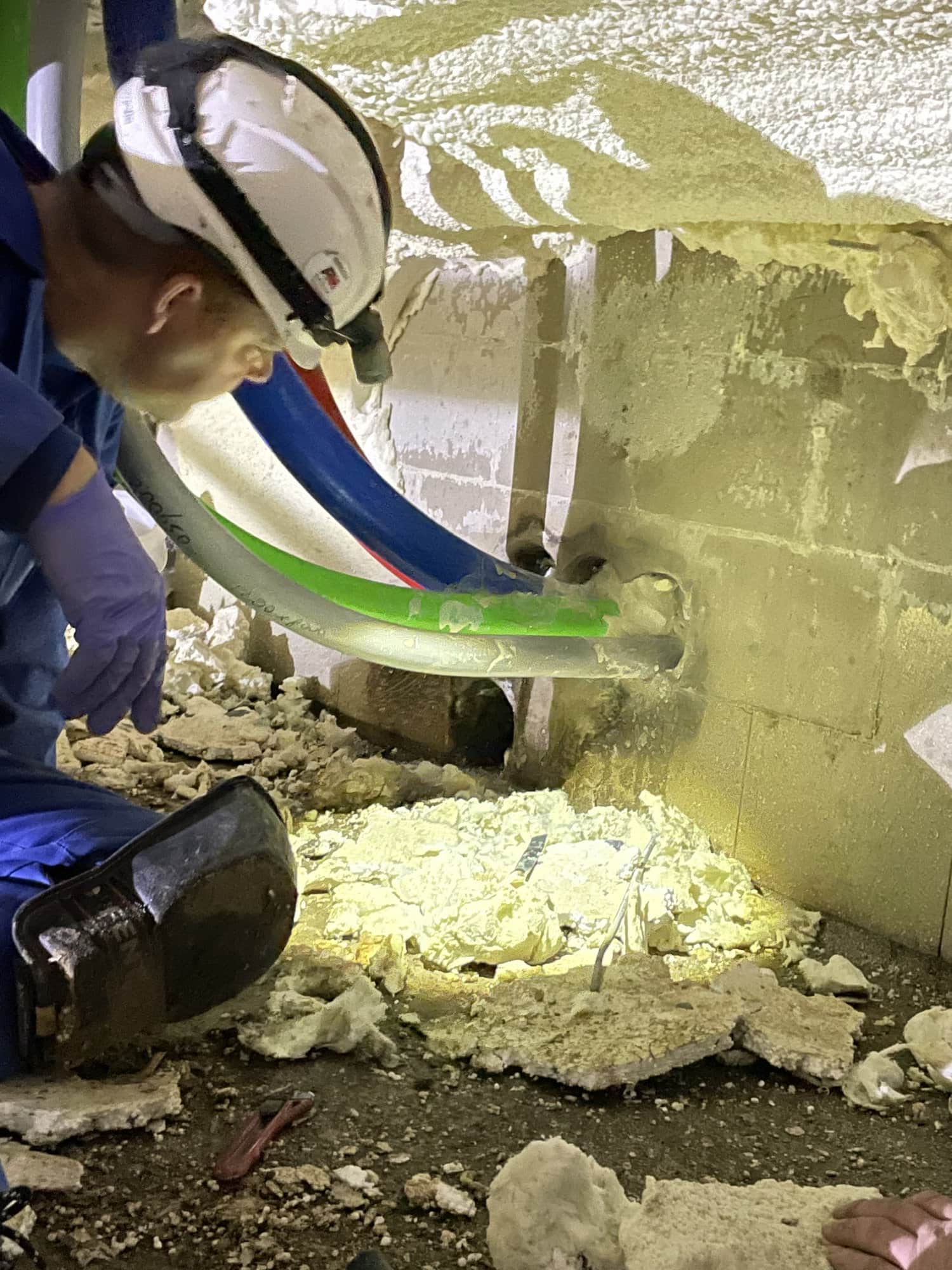
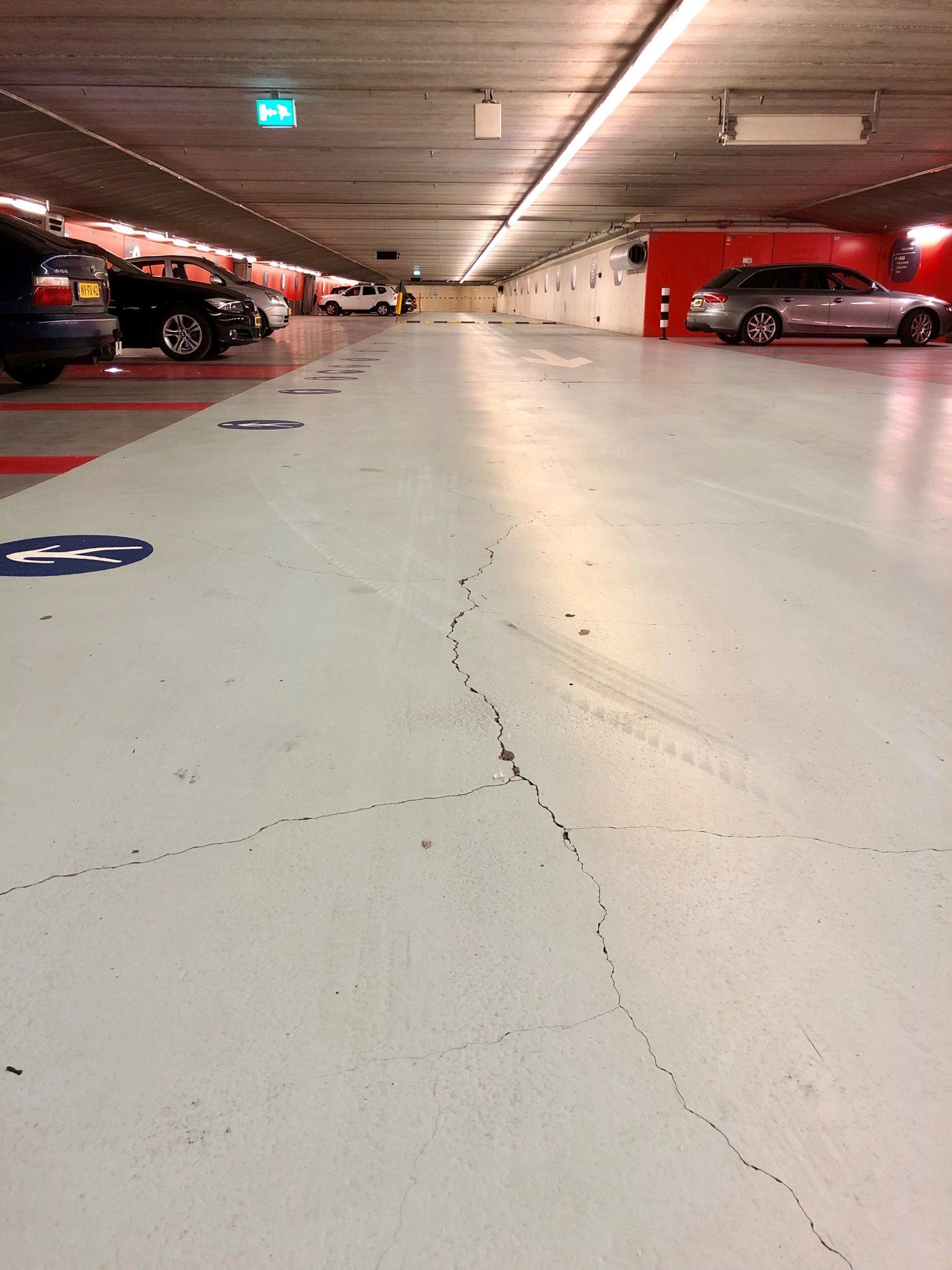
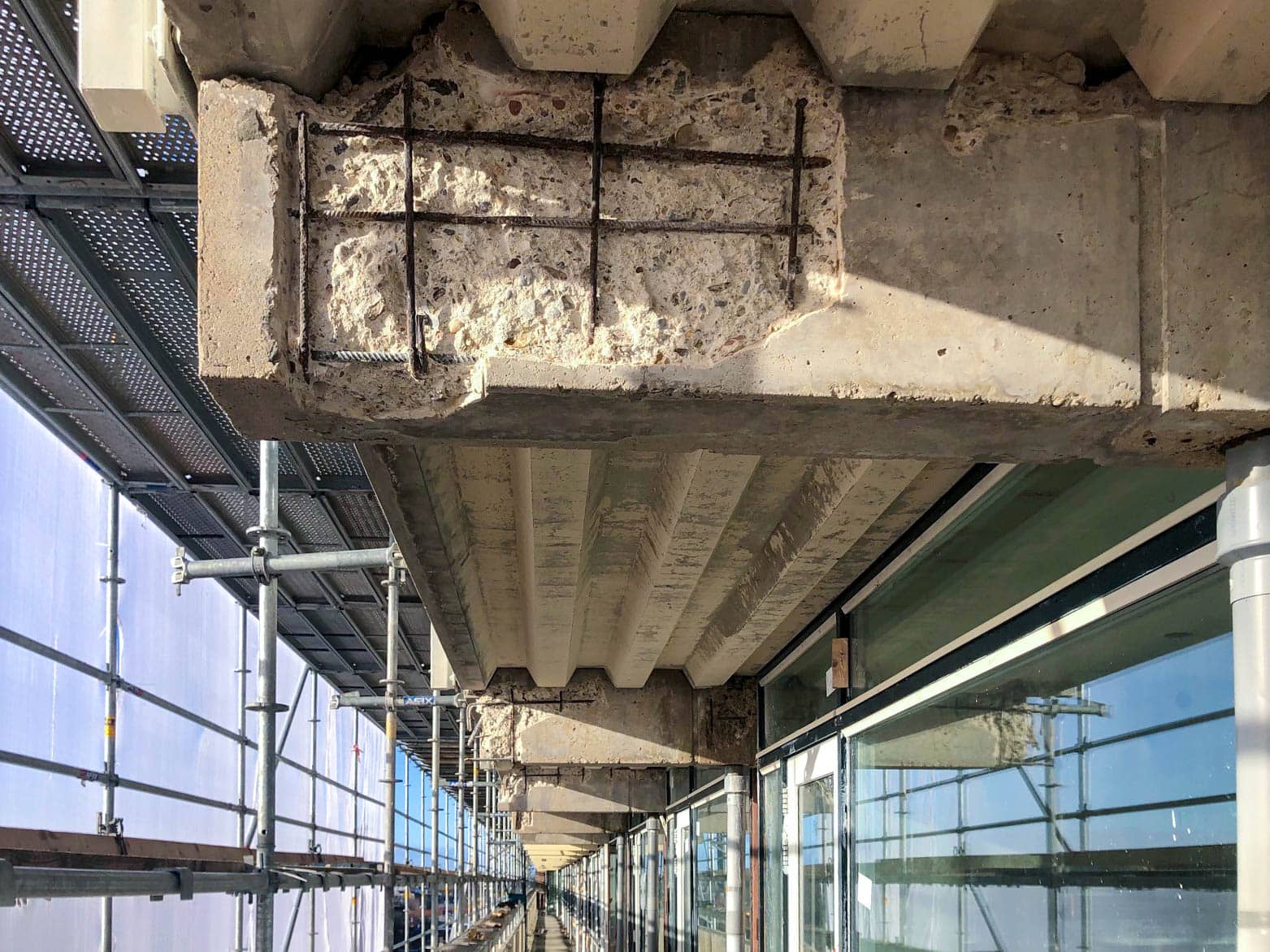
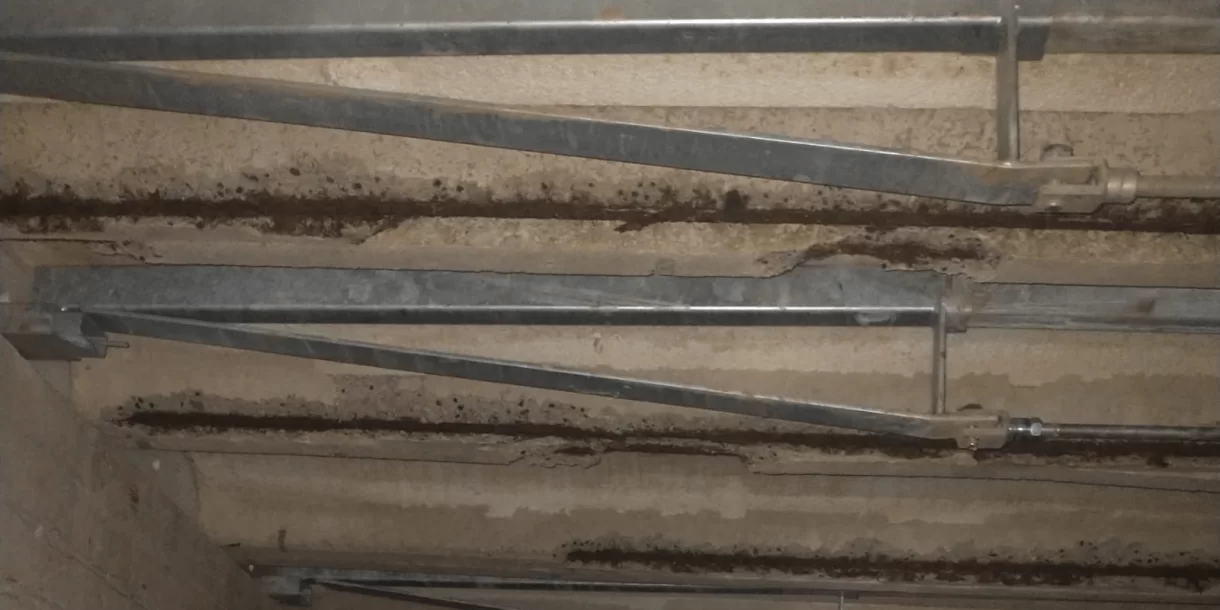
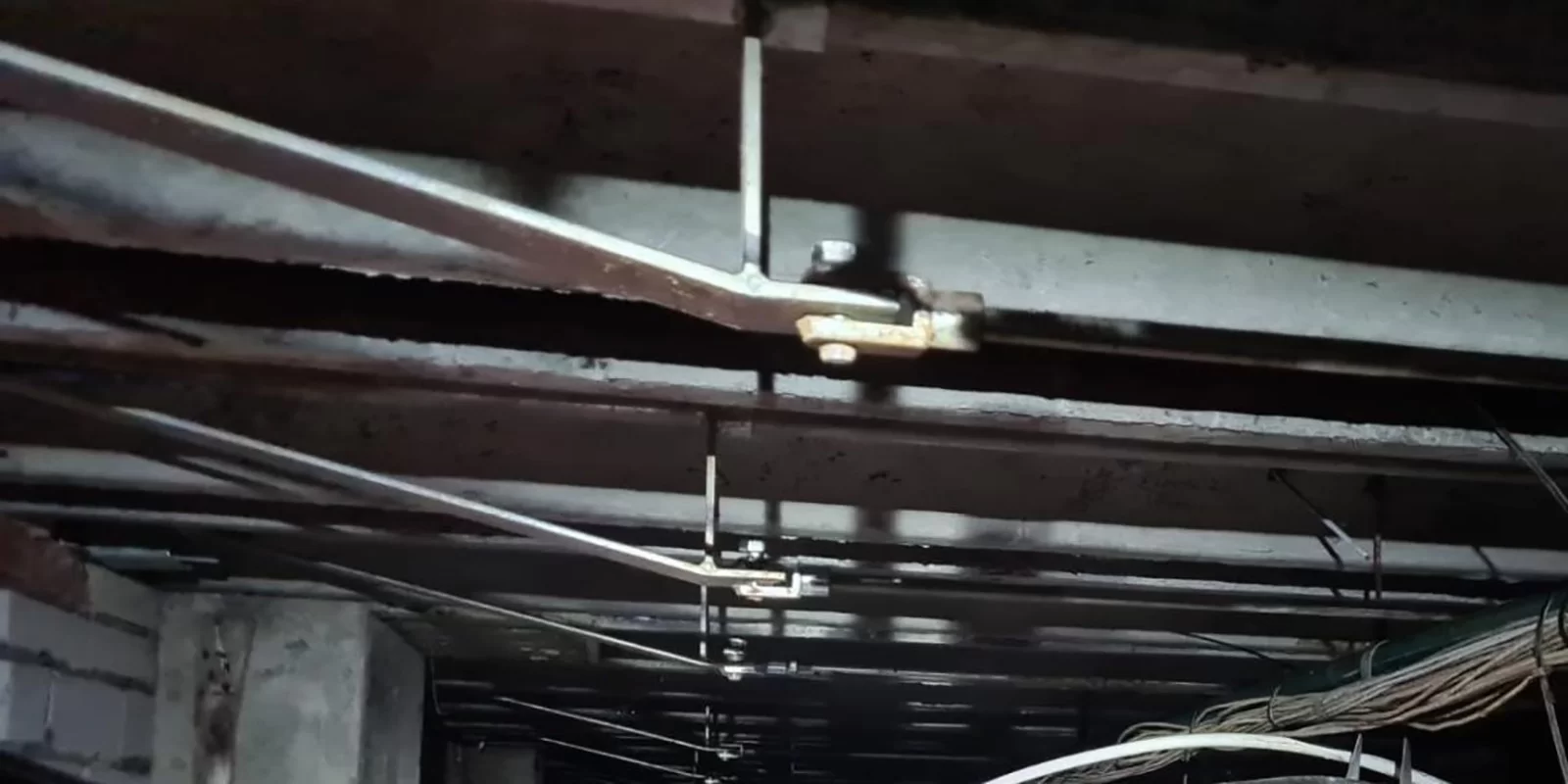
Chloride damage affects concrete structures from within. It occurs when chlorides – substances found in seawater, de-icing salt, and certain chemicals – come into contact with the reinforcing steel in concrete. These chlorides react with the steel, causing it to rust. This leads to expansion of the steel, which in turn causes cracks in the concrete. In other words: chloride damage occurs in the concrete. It is also referred to as concrete rot or carbonation of concrete.
What are the Consequences of Chloride Damage to Concrete?
The consequences of chloride attack are not only visible on the exterior but also very dangerous. Below, we delve deeper into all the consequences of chloride damage to concrete.
Weakening of the Structure
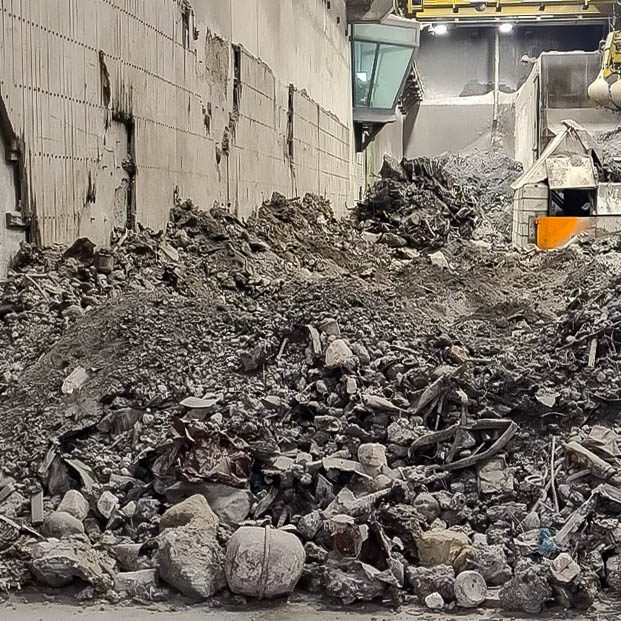
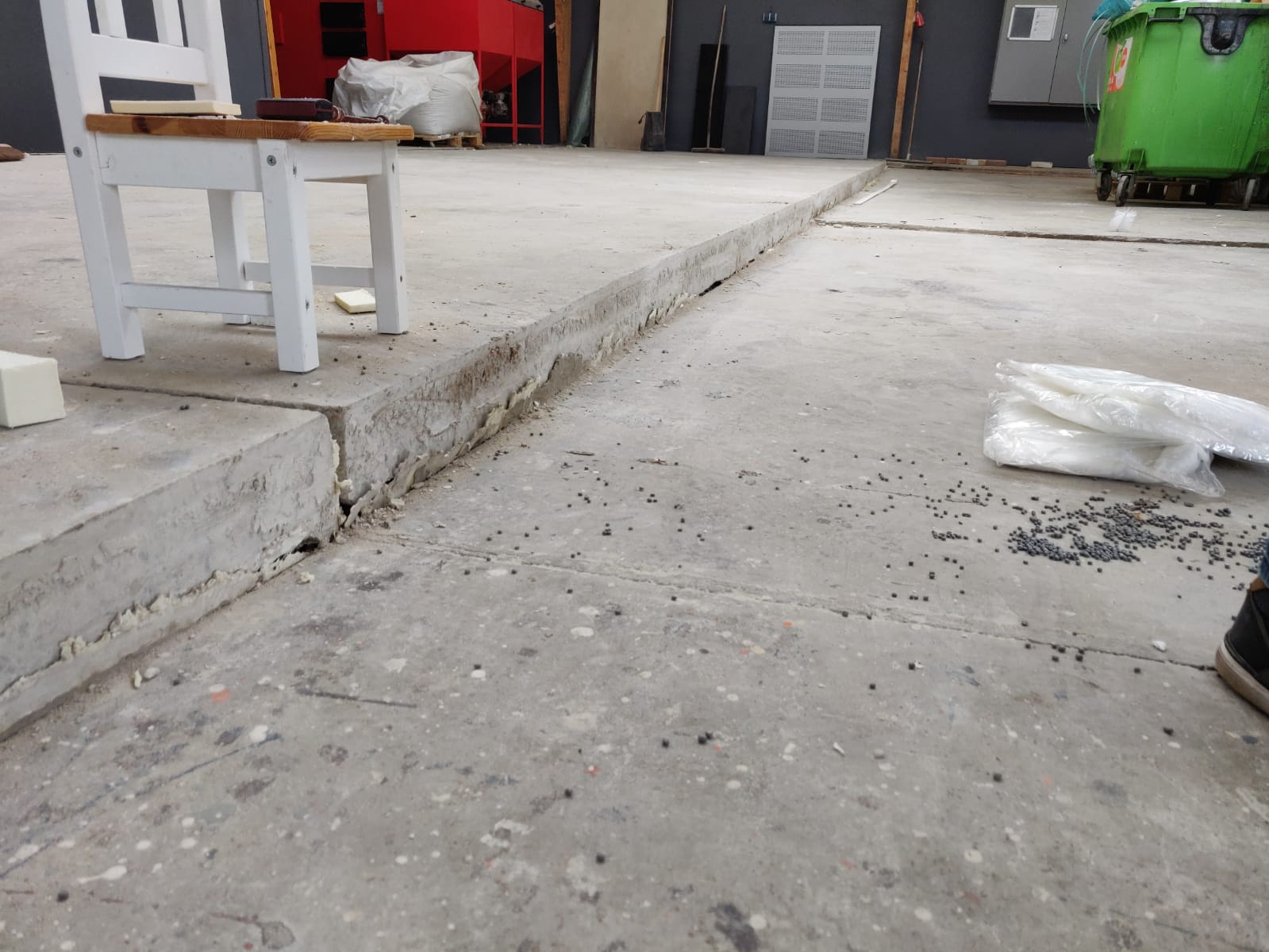
Chloride ions attack the reinforcing steel, making the concrete brittle and porous. This results in cracks, powdering, and crumbling of the concrete surface. The corrosion of the reinforcing steel also reduces the load-bearing capacity of the structure, leading to crack formation, deformation, and possibly even collapse.
Economic Burdens
Repairing concrete structures affected by chloride is complex and expensive. Regular inspections, repair work, and possible renovation are necessary to ensure safety.
Chloride damage makes concrete structures less usable for a shorter period, requiring earlier replacement or repair, which incurs additional costs. Buildings and roads with this damage also lose significant value, making them more difficult to sell or finance.
Environmental Effects
The corrosion of reinforcing steel releases harmful substances, such as salts and metals, which pollute water and damage nature. Concrete production also requires a lot of energy, leading to waste and increased CO₂ in the air when we replace damaged concrete structures.
Societal Impact
Chloride damage can eventually cause serious accidents, such as collapses of buildings and bridges. This can result in injuries or even fatalities. People may also lose confidence in the safety of buildings and roads if such accidents occur.
Traditional methods often fail
Traditional methods for repairing concrete affected by chlorides are often not effective enough. These methods include, for example, injecting epoxy resin into the concrete or completely replacing the affected concrete.
These approaches often do not fully solve the problem and are not sustainable in the long term. The chlorides remain present in the concrete, which means that the damage will recur in the future.
How Can Chloride Damage to Concrete be Solved Effectively?
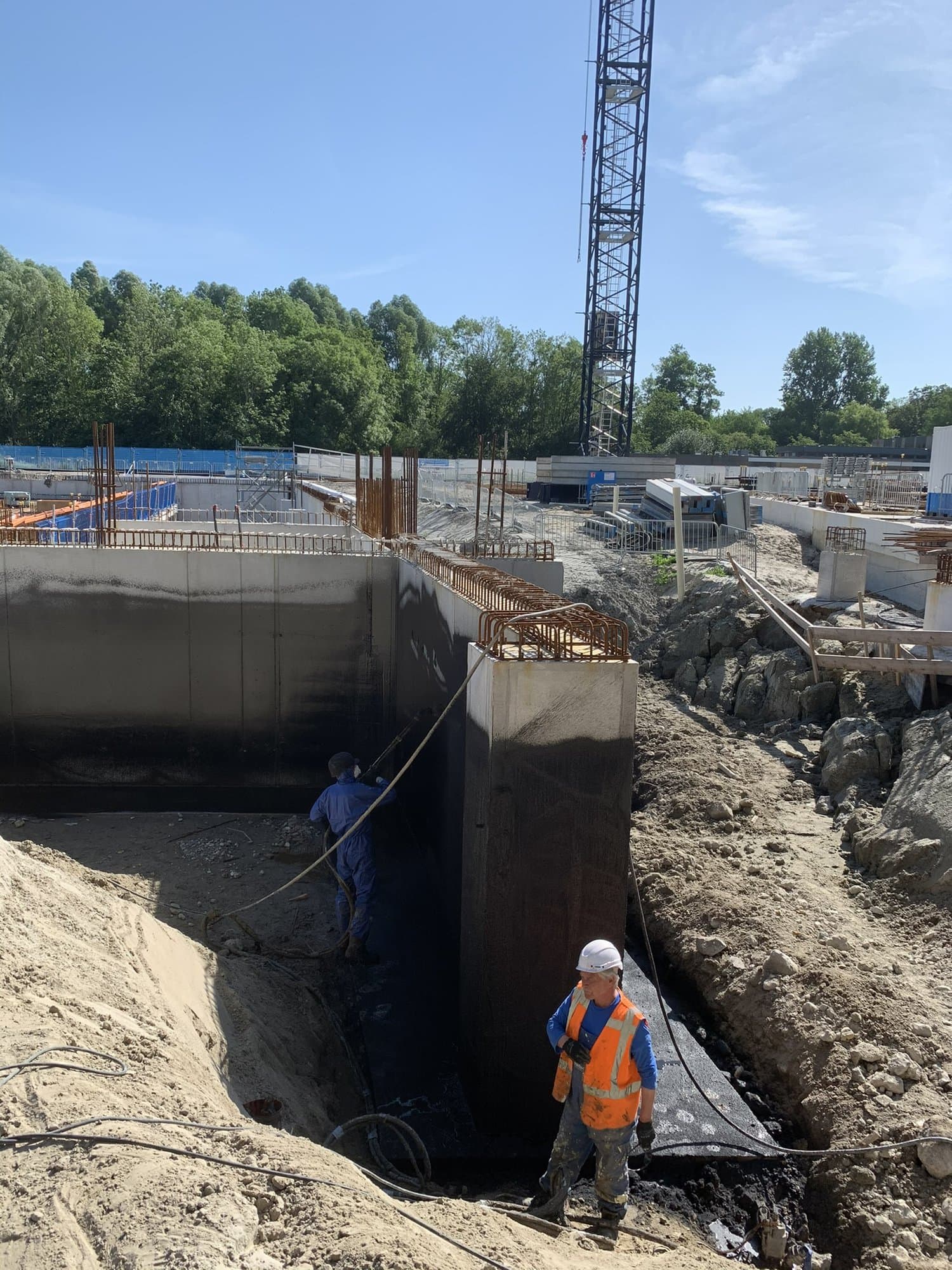
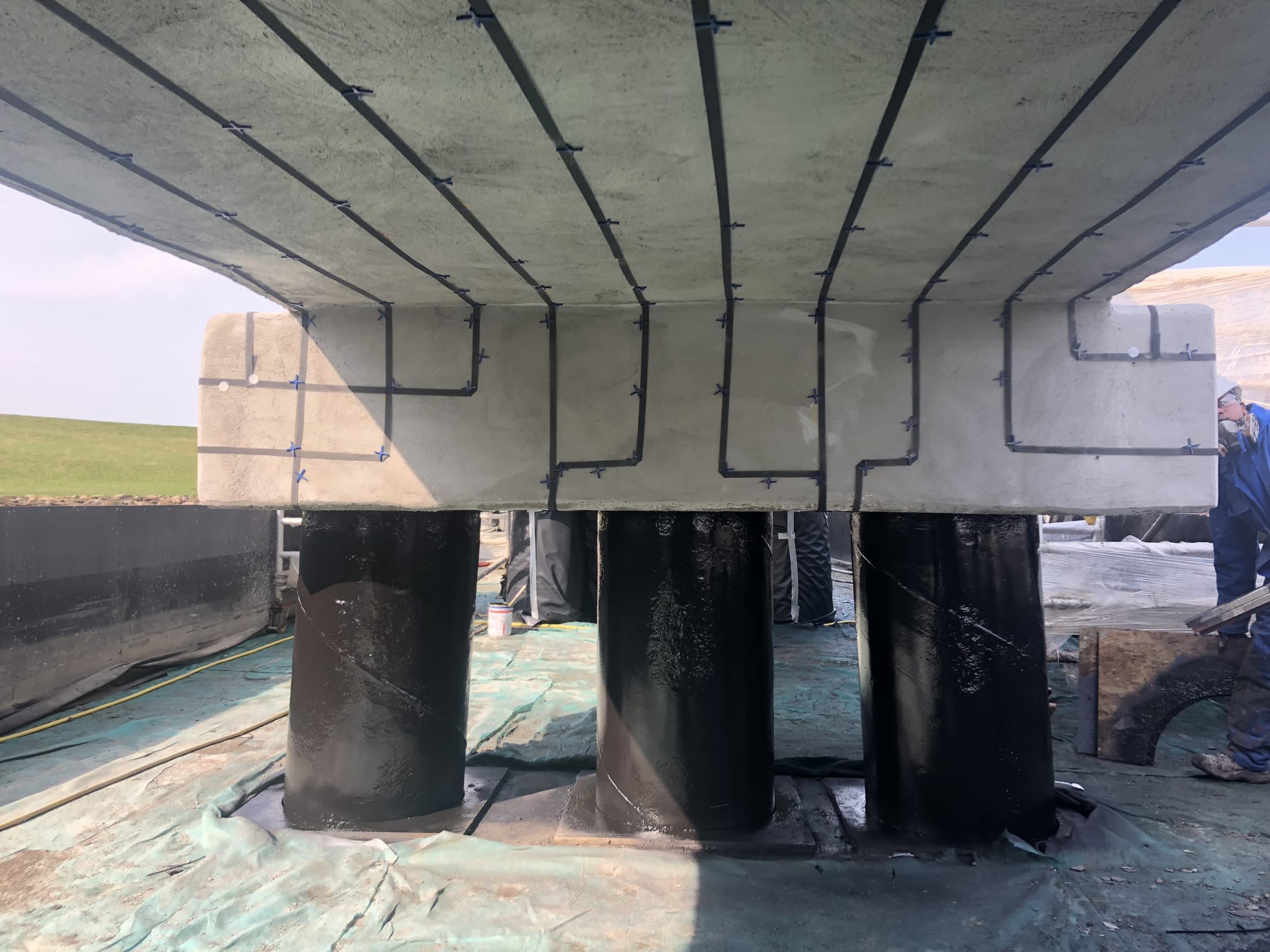
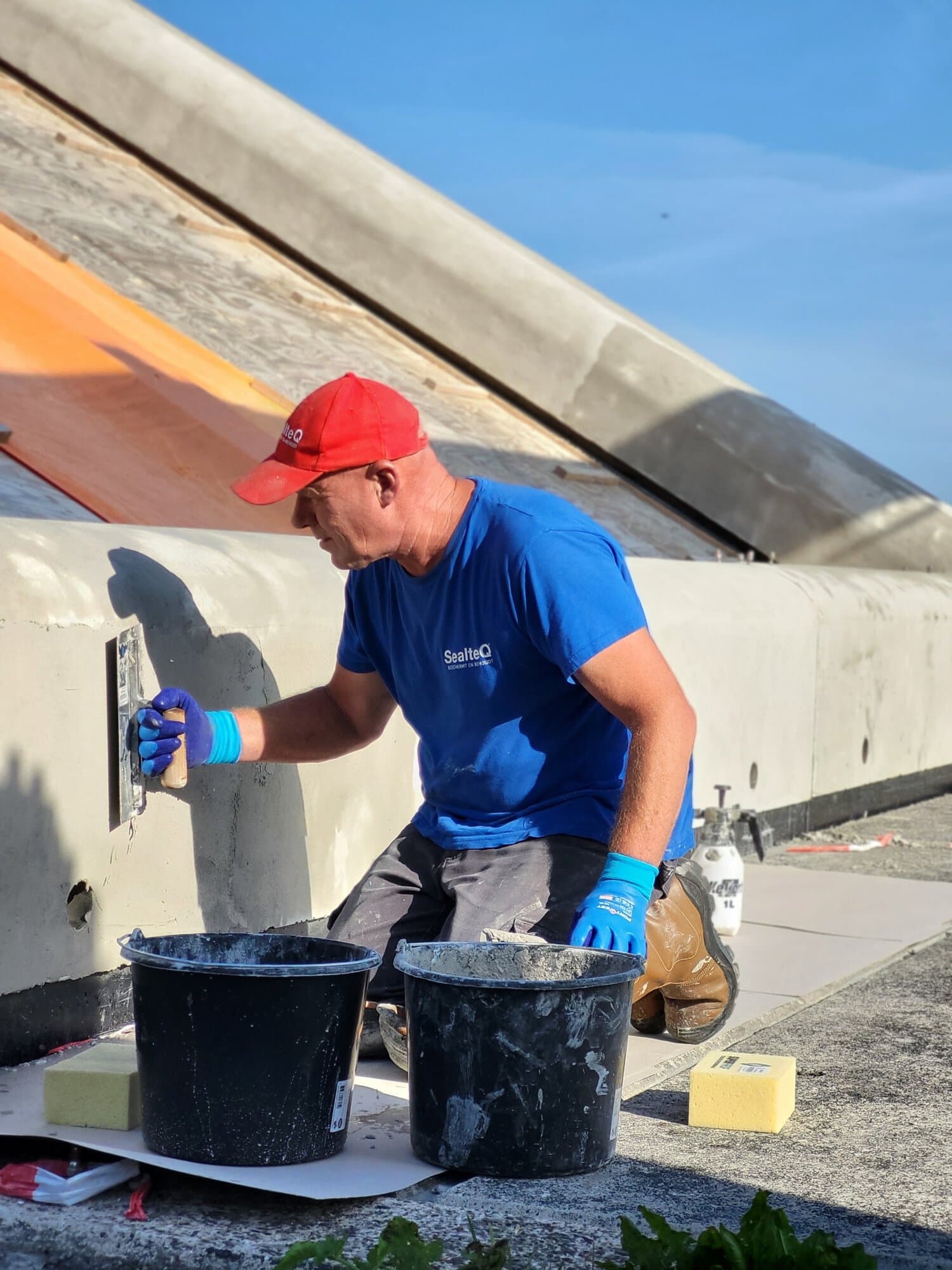
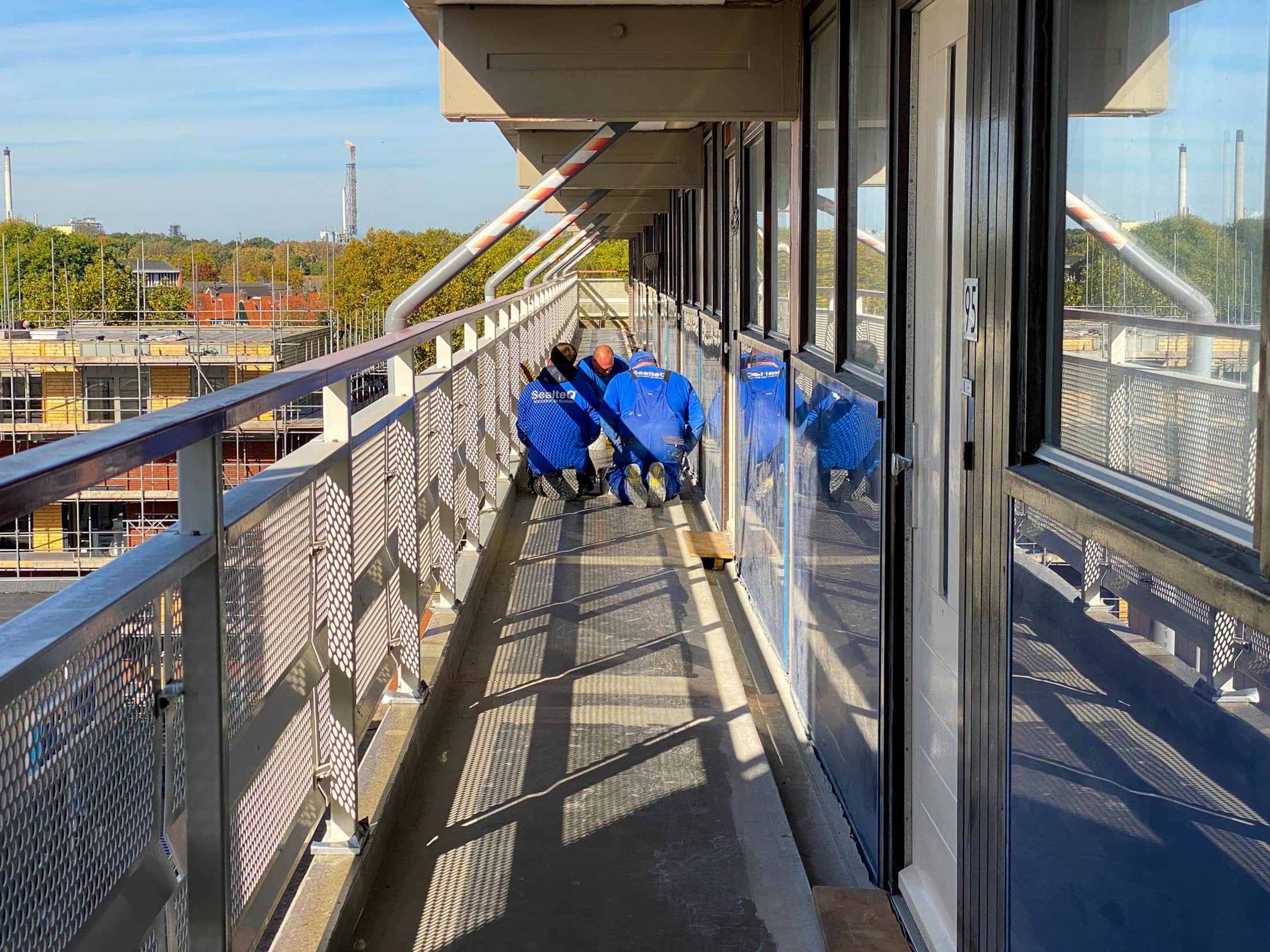
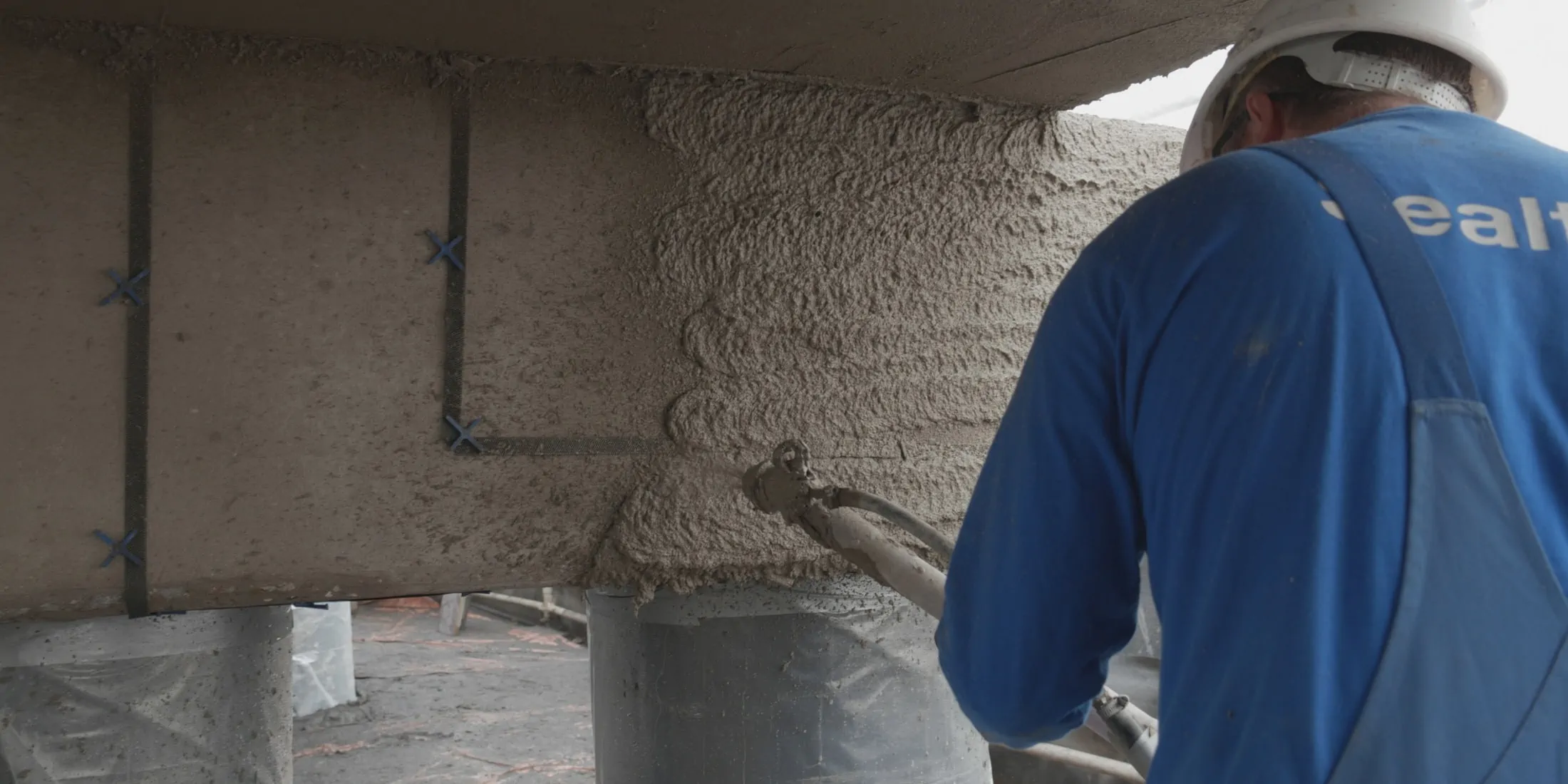
Innovative solutions for concrete repair, such as cathodic protection in combination with shotcrete are effective.
These advanced techniques for concrete renovation offer a sustainable solution for chloride damage by protecting the concrete structure against further corrosion and restoring structural integrity.
Can chloride damage to concrete be prevented?
The quality of the concrete plays an important role in preventing chloride damage. In addition to using reinforcement as a defense mechanism, concrete also has its own protective measure: the chloride class, also known as the environmental class. This class indicates how well concrete can withstand attack by chlorides, substances found in seawater, de-icing salts, and certain chemicals.
Why is the Chloride Class Important?
Choosing the right chloride class is important when designing and constructing concrete structures, especially in areas where the risk of chloride attack is high. By taking into account the expected chloride load, we can select concrete that is optimally resistant to these harmful substances.
Read more about the environmental classes of concrete here.
How can SealteQ help?
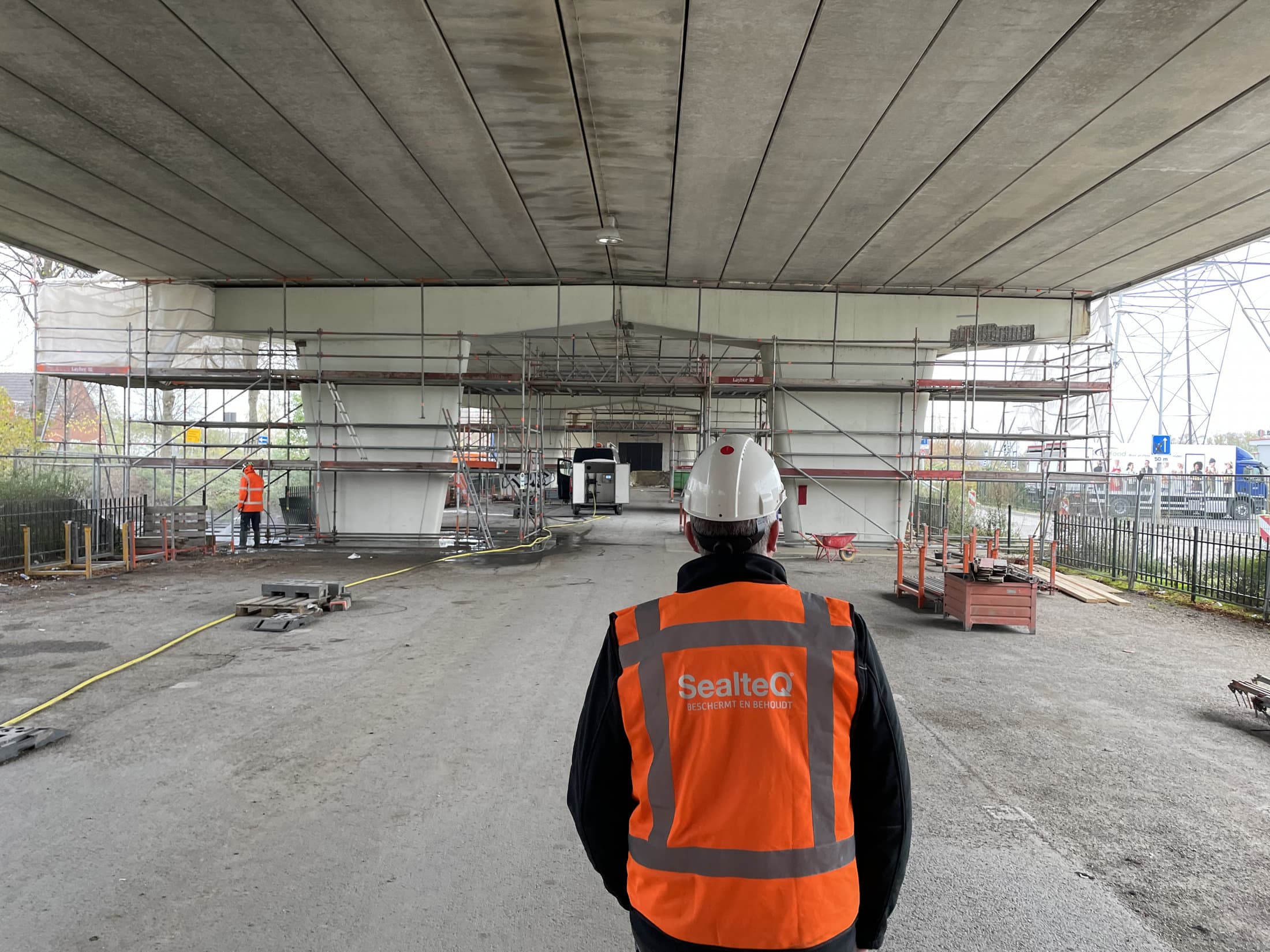
SealteQ is a leading company in concrete renovation and offers specialized solutions for chloride damage. With our expertise in cathodic protection and shotcrete, we can effectively repair and protect concrete structures against further damage. Our experienced team is ready to provide tailored solutions that meet all the needs of your project, from inspection to execution and aftercare.
What sets us apart is our focus on sustainability, reflected in our CSR policy. Our commitment to safety is evident in our obtained certificates. We strive to use only the highest quality concrete, and our solutions are designed with long-term durability in mind. Through our professional approach and use of sustainable materials, we ensure a longer lifespan for your concrete structures.
Curious about how SealteQ can help you solve chloride damage to your concrete structures? Contact us for a free consultation. Together, we ensure sustainable solutions and a longer lifespan for concrete structures.