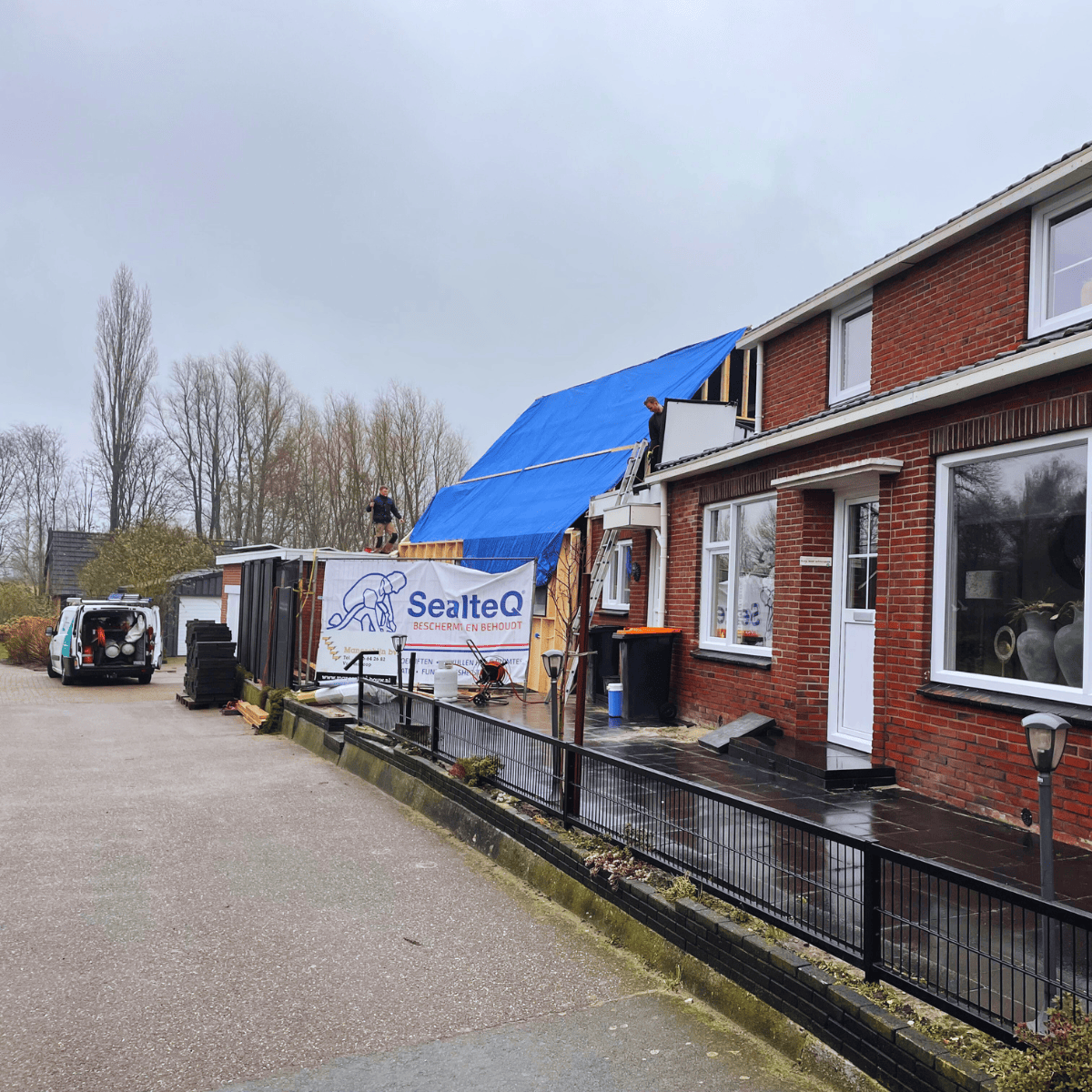
In a recent project in Daalerveen, SealteQ SLS specialists played a crucial role in the foundation repair of a building that had suffered extensive damage due to uneven settlement and a partially collapsed foundation. The issue with the home's foundation required a well-thought-out approach to prevent further damage while minimizing disruption to the residents during the foundation repair operation.
Foundation repair in Daalerveen
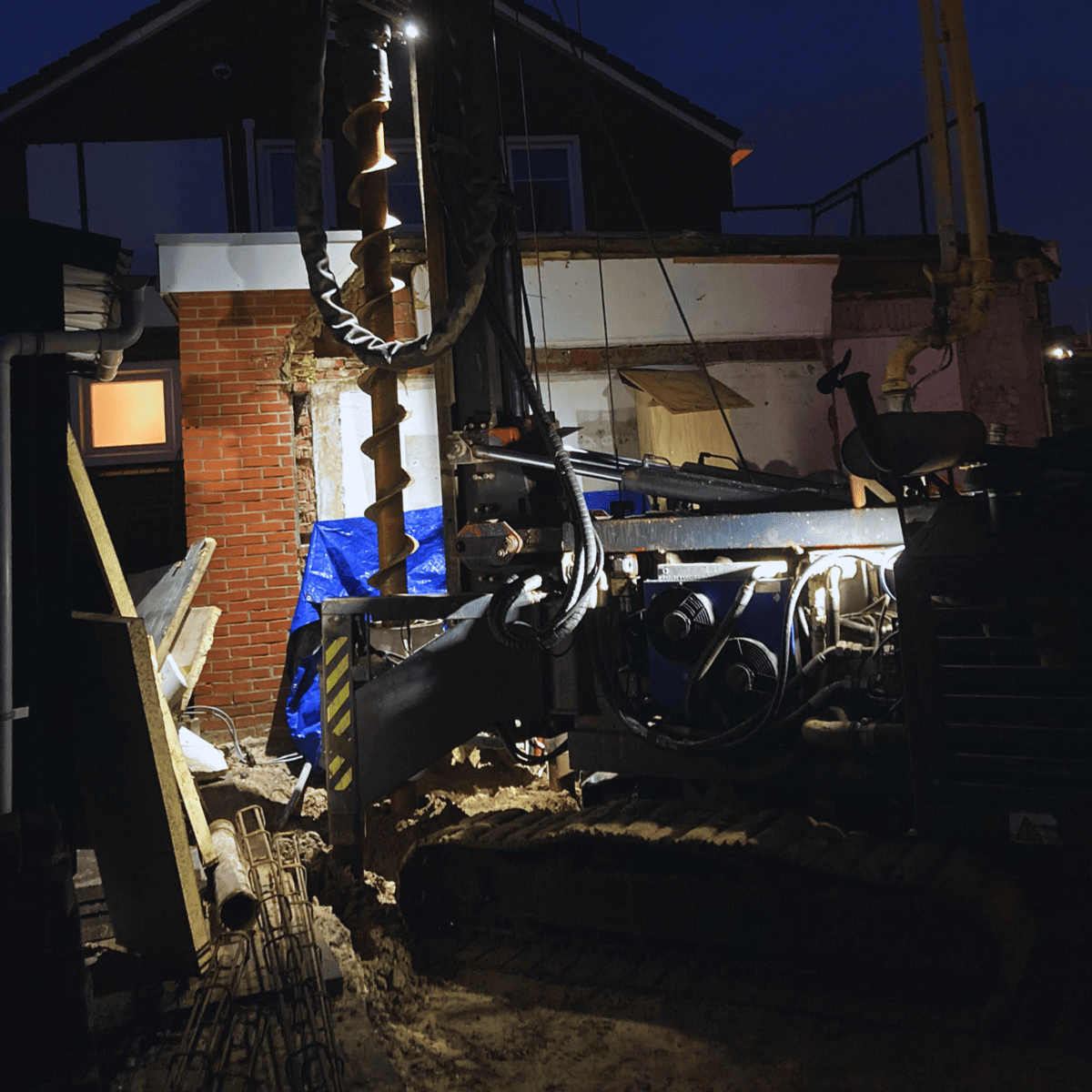
The building historically consists of three sections, each with its own type of foundation. The second part of the house had begun to sag against the main building due to a locally collapsed foundation, causing significant damage. Foundation repair using the table method was applied to this middle section. The foundation was rebuilt using screw mortar piles. To prevent disturbance, this was done without vibrations. For the main building and the third part of the house, our specialists opted for in-situ soil improvement through injection techniques. Thanks to a collaboration with Van Dijk Maasland (VDM), specialists in foundation repair using the table method, we are able to offer the complete range of foundation repair techniques.
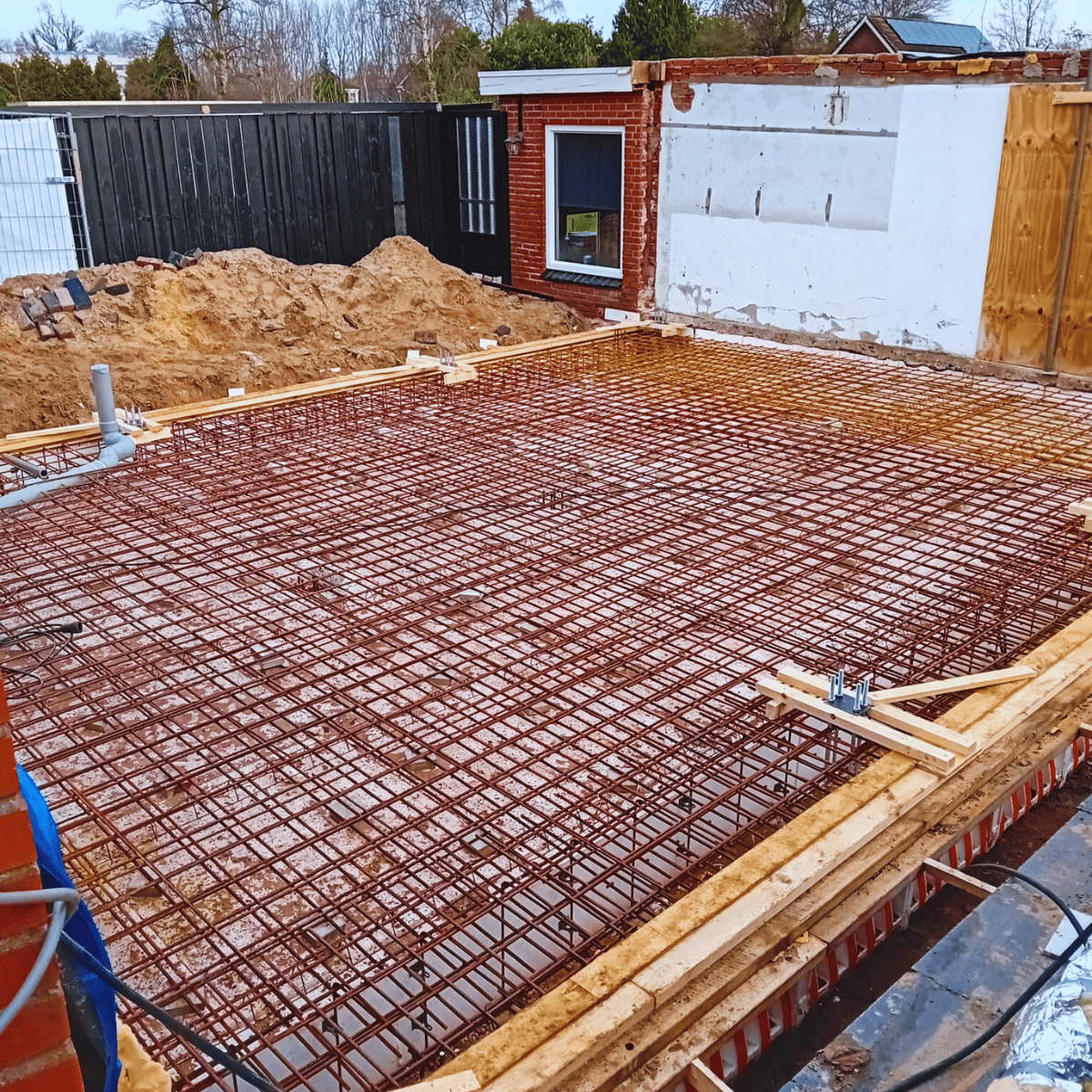
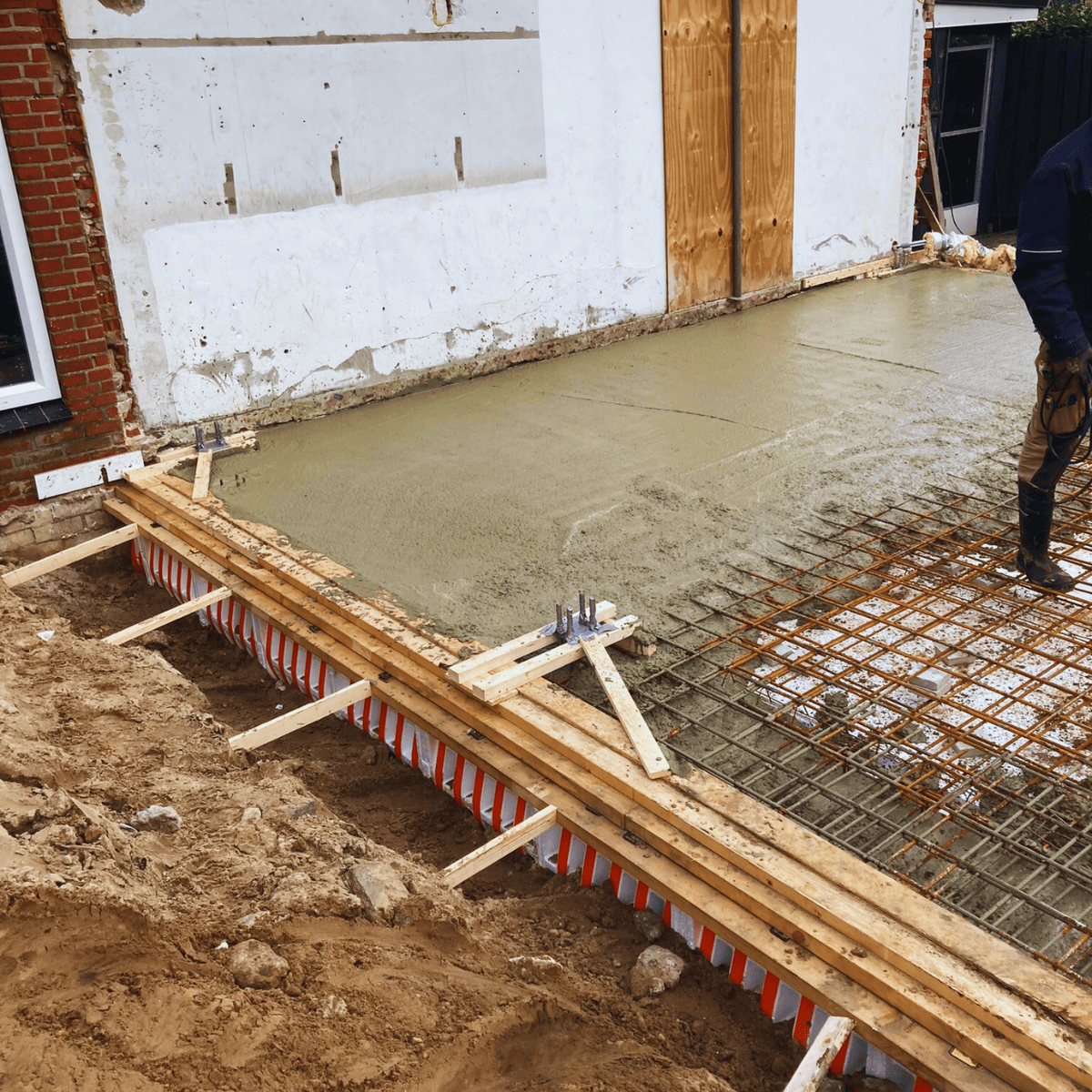
The foundation repair of the house’s middle section was accomplished by first carefully removing the roof structure, walls, and ground floor. Temporary provisions were made for piping and accessibility, allowing the rest of the house to remain inhabited. After completing the preparatory demolition and excavation work, vibration-free screw mortar piles were installed to create a new foundation. After installing the formwork and reinforcement of the edge beam, concrete was poured. The EPS insulation makes the new floor suitable for underfloor heating. Finally, the middle section could be rebuilt using steel trusses placed on the floor construction. This has restored the building’s structural integrity.
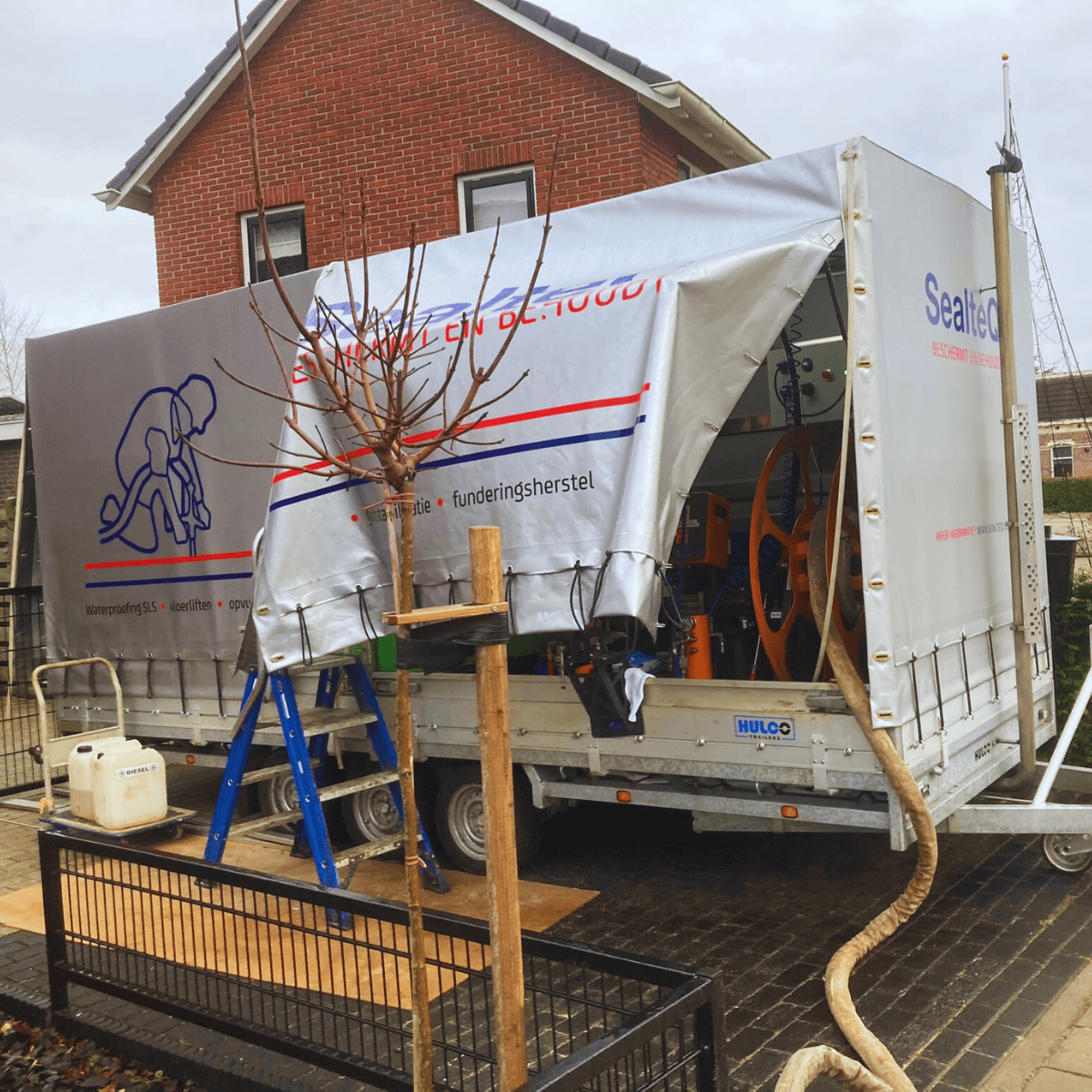
To ensure the stability of the subsoil beneath the existing foundation of the front and back house, SealteQ SLS specialists opted for soil injection. The process included filling any hollow spaces under the foundation and increasing the load-bearing capacity beneath the foundation of the load-bearing interior and exterior walls.
Thanks to the unique coupling system of our injection lances, injection can be performed from the crawl spaces without drilling through or damaging the existing floor fields. With this careful approach, the load-bearing capacity of the subsoil has been stabilized and future subsidence has been minimized. As a result, the building’s foundation has been safely and sustainably restored.