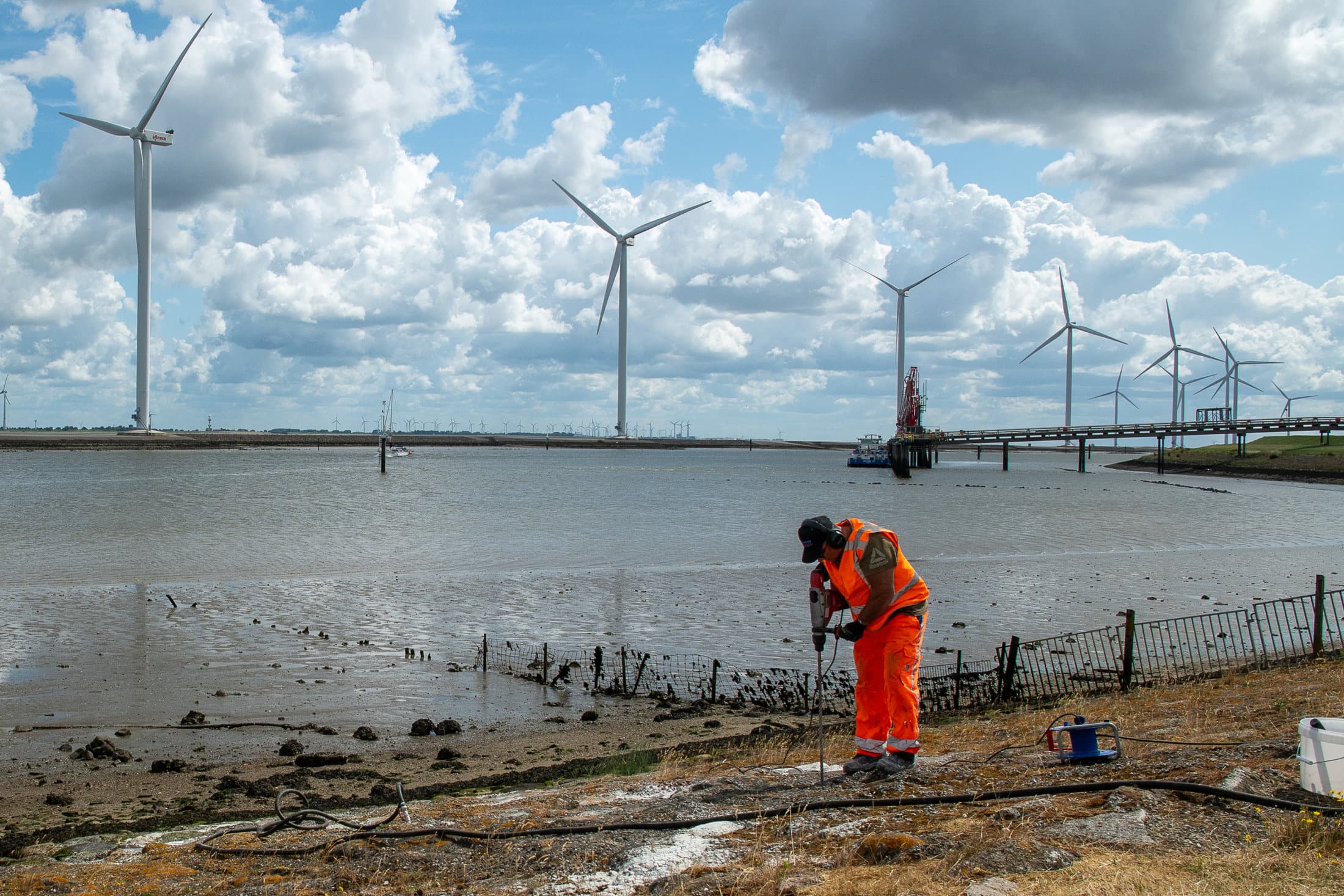
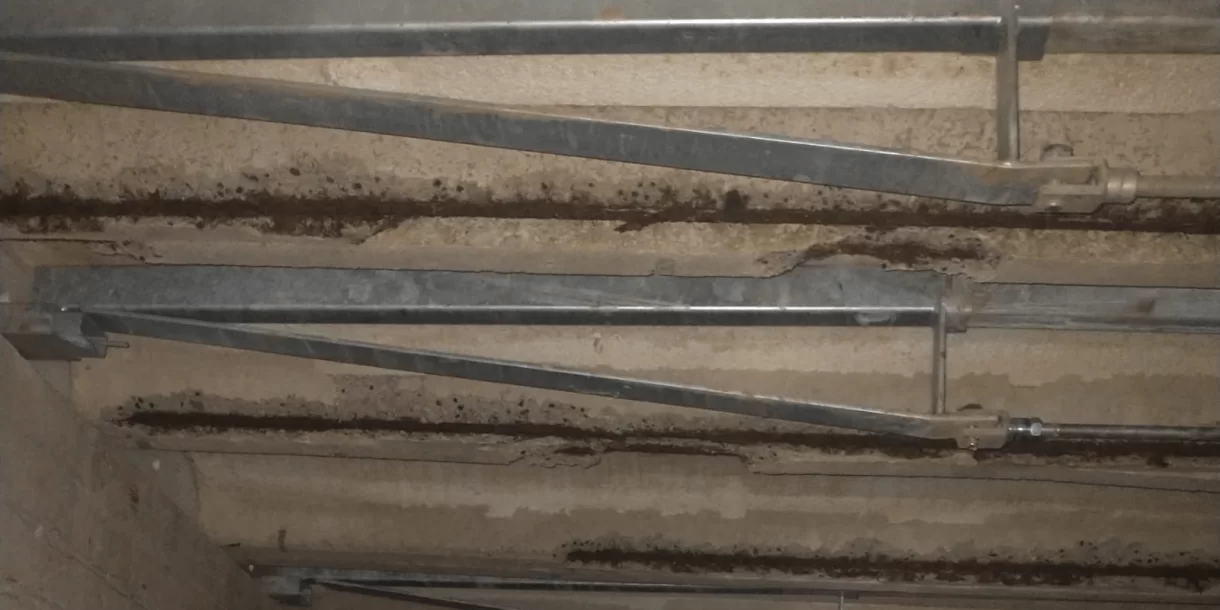
Are you dealing with foundation problems? Foundation problems can have serious consequences for the safety and stability of a structure. Whether it concerns cracks in the foundation, subsidence, or reduced load-bearing capacity, recognizing these issues is crucial. Read all about the causes, consequences, and possible solutions, and discover how SealteQ can help with a sustainable and professional approach.
Foundation Problems
What are foundation problems?
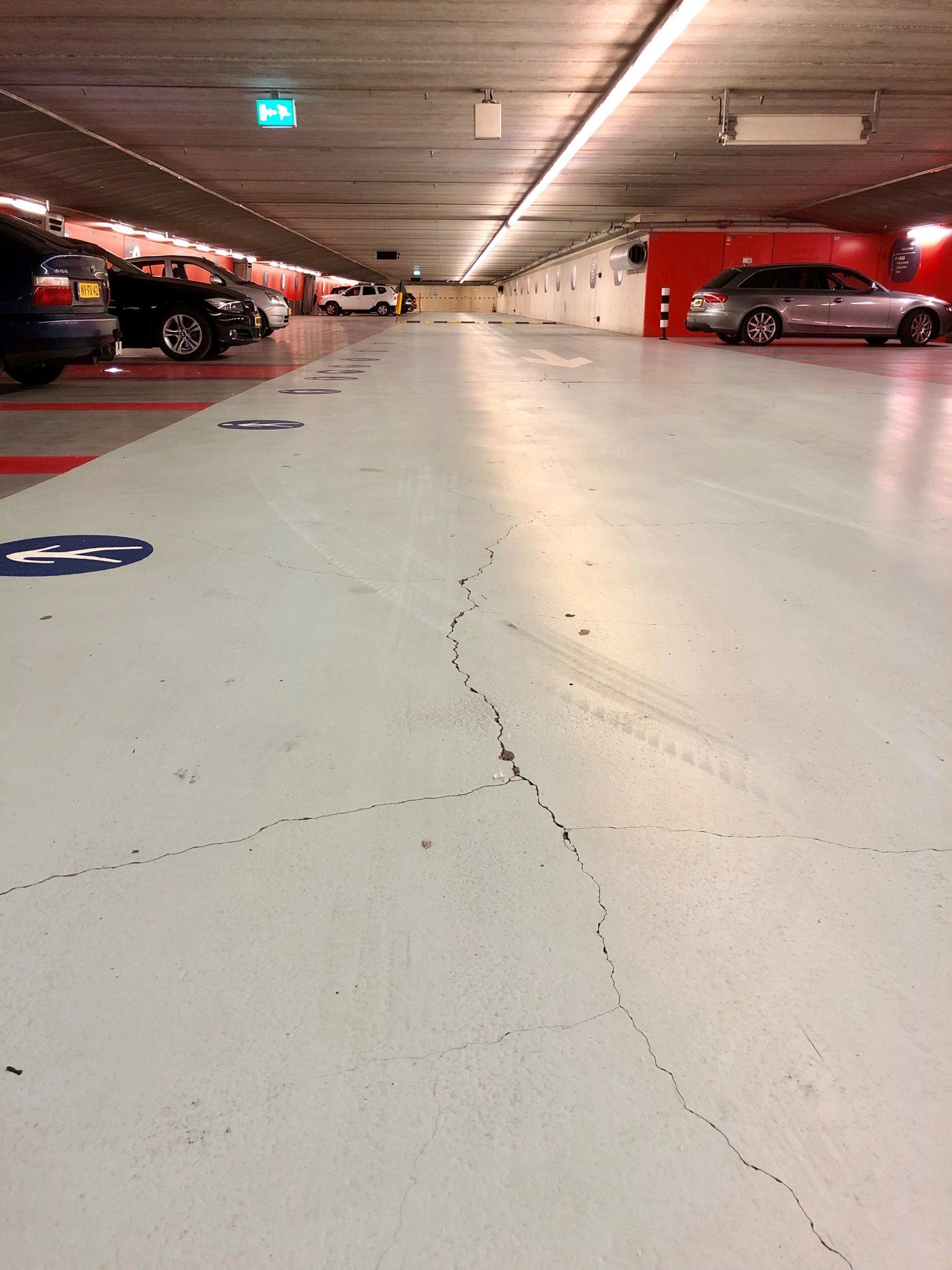
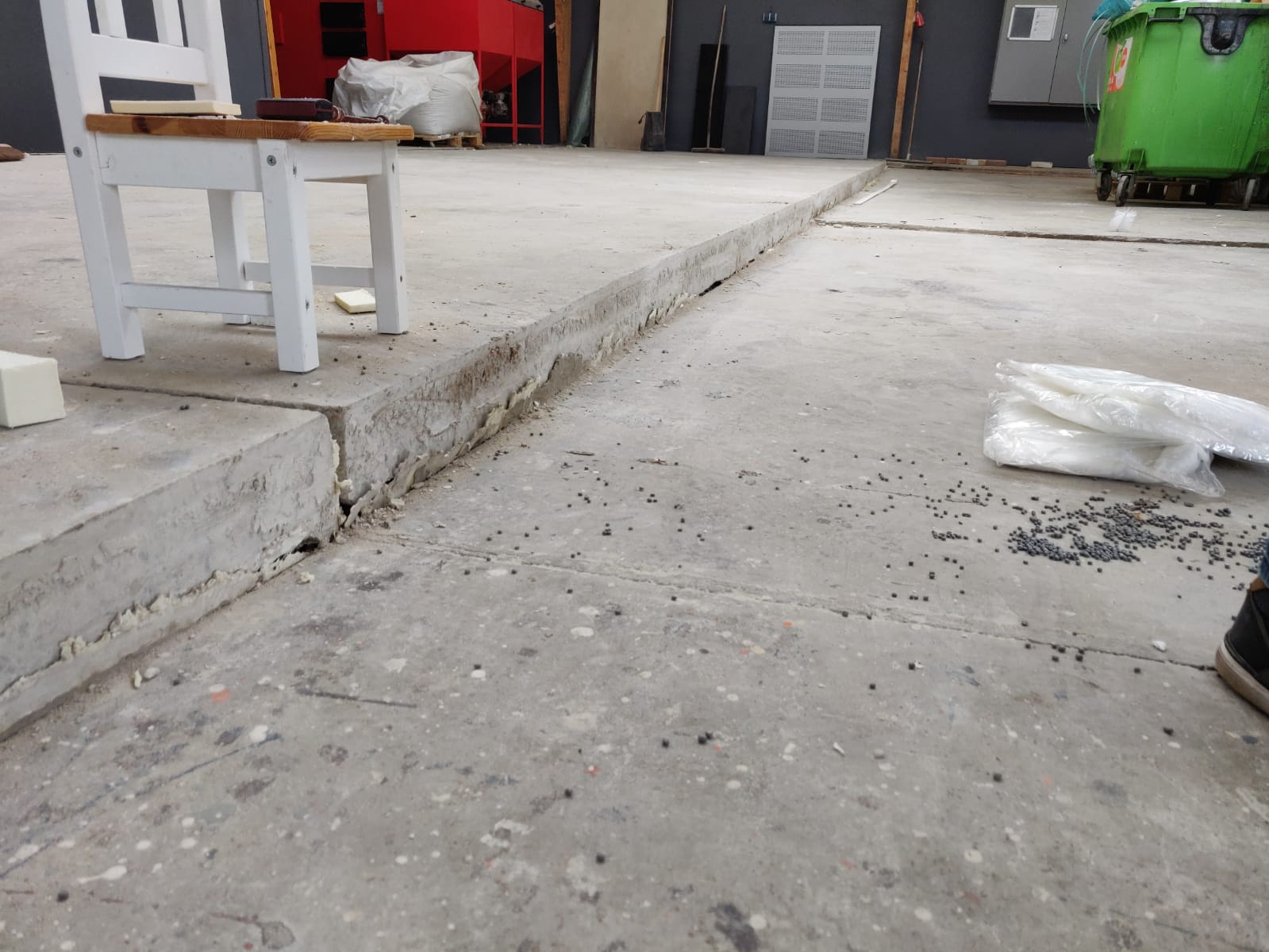
When the foundation of a building or structure no longer provides sufficient load-bearing capacity, foundation problems can arise in the form of cracks and subsidence in the foundation, and even instability of the structure. These issues are often caused by external factors such as land subsidence, climate change, and fluctuations in groundwater levels.
Recognizing Foundation Problems
There are several signs that may indicate foundation problems.
- If you see cracks in walls or floors, this may indicate uneven loading.
- Settlement issues with uneven drops in the foundation may indicate a tilt.
- Rising damp or damp patches on walls are signs of failed waterproofing and a foundation that is not watertight.
- If you also see material that appears to crumble, this can also be a sign of foundation problems.
Identifying foundation problems early is important to prevent more extensive damage and higher repair costs.
Foundation Risk Areas
In the Netherlands, certain regions are more susceptible to foundation problems, such as peat and clay areas. The Kennis Centrum Aanpak Funderingsproblematiek (KCAF) designates these regions as risk areas. These areas are characterized by an unstable soil structure that is prone to land subsidence and water-related issues. The risk of foundation problems is particularly high in the west and north of the Netherlands.
Risks to your Property
If the following situations apply to you, we recommend engaging our specialists for foundation assessment and repair.
- You have recently purchased a home and there may be problems with the foundation. Look for cracks in walls, subsidence, and sticking doors, and consult old construction drawings and soil reports. For serious issues, we recommend repairing the foundation, which we can also carry out for you.
- Your neighbors have foundation problems with their home. This may affect your property, especially where there are party walls or similar soil conditions. Look for cracks or subsidence and have an inspection performed.
Causes of foundation problems
Foundation problems arise from a combination of factors that are highly dependent on environmental conditions and human influences.
- Climate change plays a major role. Increasingly extreme weather conditions, such as heavy rainfall and prolonged drought, can directly impact the stability of the ground and foundations.
- In areas with peat and clay soils, as in parts of the Netherlands, land subsidence moreover leads to ground settlement and reduced stability.
- Other causes include overloading the foundation or errors during construction, which make the structure more vulnerable.
- Natural processes such as peat oxidation and differential settlement of the subsoil can also lead to cracks and subsidence.
Together, these factors form a complex interplay that can seriously compromise the integrity of foundations.
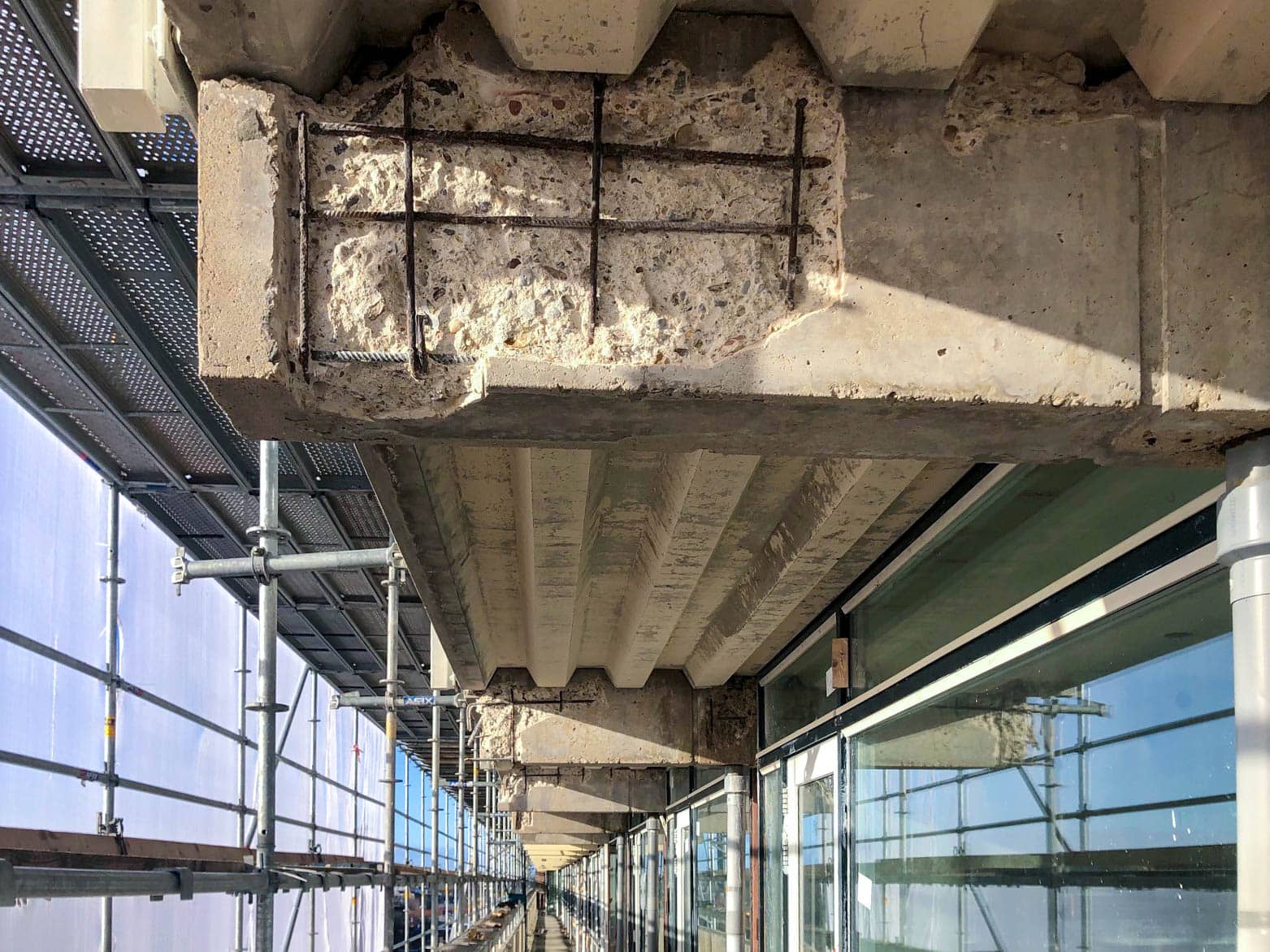
Consequences for the Structure
The consequences of foundation problems are far-reaching, ranging from structural instability to aesthetic damage:
- Foundation cracks are not only a visual problem but may also indicate more serious structural damage.
- Loss of load-bearing capacity of the foundation can jeopardize the safety of the building or structure.
- Subsidence can lead to tilt, uneven floors, and cracks in walls and ceilings.
Frequently asked questions about foundation problems
How Can You Tell there are Foundation Problems?
You will notice foundation problems through cracks, subsidence, or moisture issues. Typical signs include cracks in facades or interior walls, uneven (sloping) floors, and sticking windows or doors. Damp patches or mold can also indicate a failing, non-watertight foundation.
Where in the Netherlands Do Foundation Problems Occur?
Foundation problems occur mainly in peat and clay areas, particularly in the west and north of the Netherlands. These regions have an unstable soil structure that is susceptible to land subsidence and groundwater fluctuations. As a result, buildings there are at greater risk of subsidence and foundation damage.
How Do You Know if your Foundation is in Poor Condition?
You can identify a compromised foundation by cracks, subsidence, and other signs of damage. For example: cracks in walls, uneven settlement causing sloping floors, sticking doors/windows, and damp or mold patches in the basement. These symptoms indicate that the foundation is no longer sound.
Where are the Main Foundation Risk Areas?
The highest foundation risks are in areas with soft soils, such as peat and clay regions in the west and north of the Netherlands. These regions are designated by experts (KCAF) as risk areas due to unstable ground that is susceptible to settlement and moisture problems.
Which Houses are at Risk of Subsidence?
In particular, older houses on a shallow foundation (“op staal”) in soft soils are at risk of subsidence. Homes built on peat or clay soils (often in the west and north of the country) are vulnerable: the soft subsoil can compact or dry out, causing the foundation to sink.
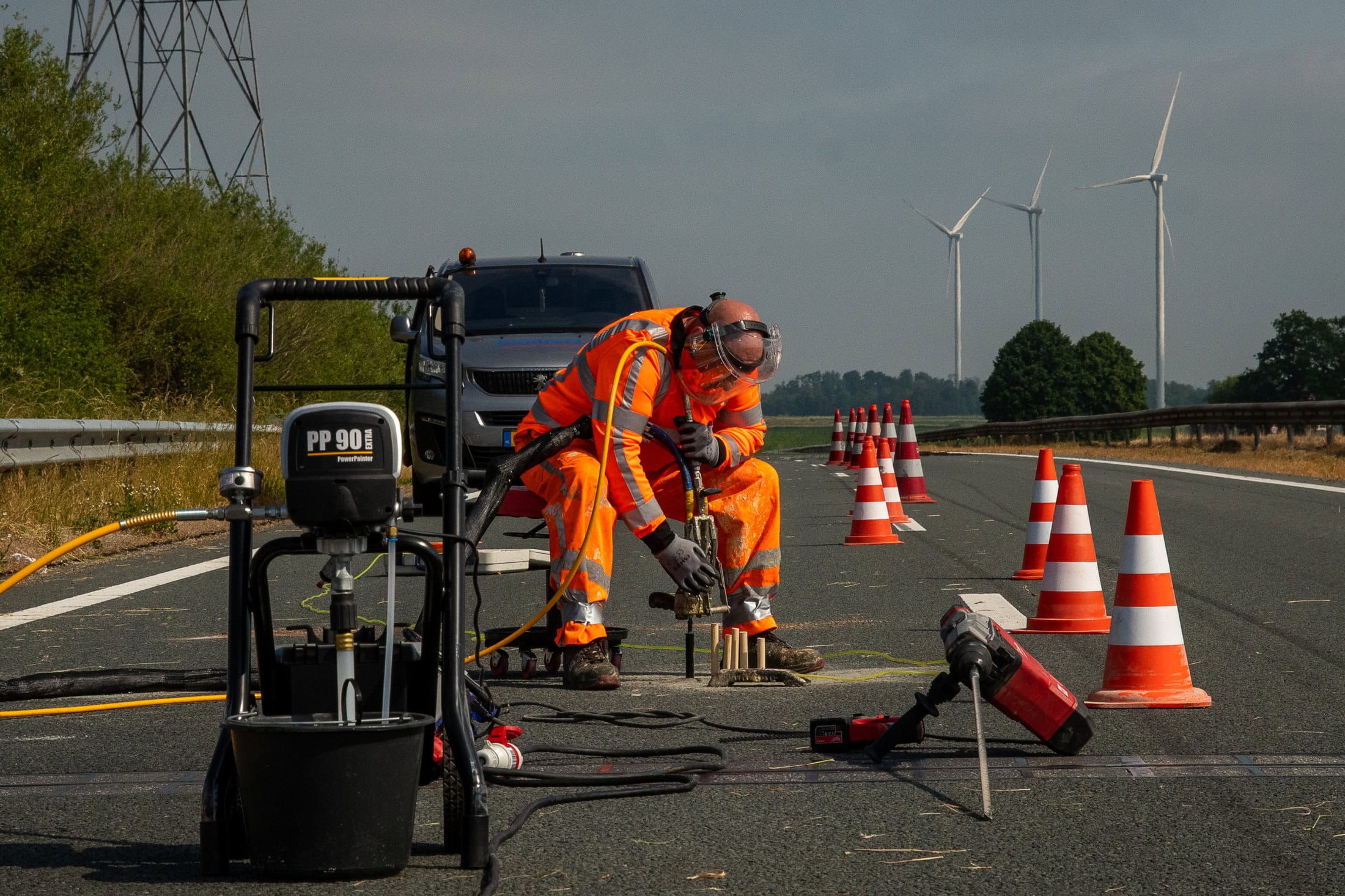
Solving foundation problems? Consult SealteQ
Have you noticed signs of foundation problems? Do not wait any longer and get contact with SealteQ for foundation repair. Our experienced specialists are ready to help you reinforce the foundation and restore it. We provide expert advice, carry out a thorough inspection, and offer sustainable solutions. With our focus on quality and innovation, you are assured of a safe and stable foundation.
Contact us today and discover what SealteQ can do for you!